
Parabolic Motion of
Projectiles
A GIF Animation
A projectile is an object upon which the only force is
gravity. Gravity, being a downward force, causes a projectile to
accelerate in the downward direction. The force of gravity could
never alter the horizontal velocity of an object since perpendicular
components of motion are independent of each other; vertical force
does not effect a horizontal motion. The result of a vertical force
acting upon a horizontally-moving object is to cause the object to
deviate from its otherwise linear path. This is depicted in the
animation below.
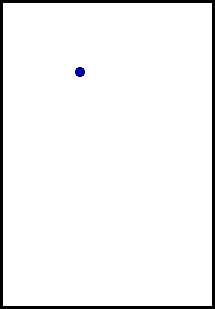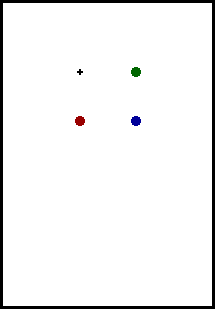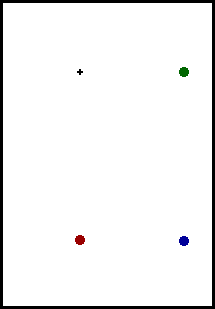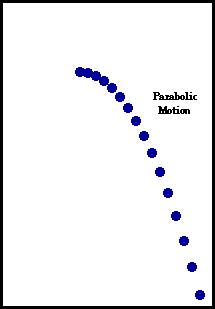
According to Newton's law of inertia, an object in motion in a
horizontal direction would continue in its horizontal motion with the
same horizontal speed and direction unless acted upon by an
unbalanced horizontal force. The animation above shows a green
sphere moving to the right at constant speed. The horizontal
distance traveled in each second is a constant value. The red sphere
undergoes an vertically-accelerated motion which is typical of an
object upon which only the force of gravity acts. If these two
motions are combined - vertical free fall motion and constant
horizontal motion - then the trajectory will be that of a parabola.
An object which begins with an initial horizontal velocity and is
acted upon only by the force of gravity will follow the path of the
blue sphere. It will travel the same horizontal distance in each
consecutive second but will fall vertically a greater distance in
each consecutive second. The result is a parabolic path as shown in
the animation above.
For more information on physical descriptions of motion,
visit
The
Physics Classroom. Specific information is available there on the
following topics:
This page was created by
Tom
Henderson of
Glenbrook South
High School.
Comments and suggestions can be sent by e-mail to
Tom
Henderson.
This page last updated on 11/16/98.
