
Longitudinal
Wave
A GIF Animation
A wave is a disturbance of a medium which transports energy
through the medium without permanently transporting matter. In a
wave, particles of the medium are temporily displaced and then return
to their original position. There are a variety of ways to categorize
waves. One way to categorize waves is to say that there are
longitudinal and transverse waves. In a transverse wave, particles of
the medium are displaced in a direction perpendicular to the
direction of energy transport. In a longitudinal wave, particles of
the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to energy transport.
The animation below depicts a longitudinal pulse in a medium.
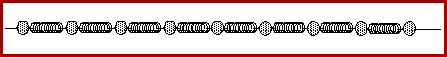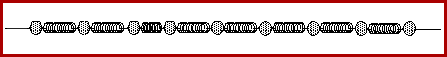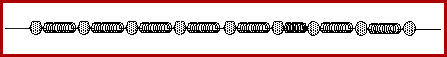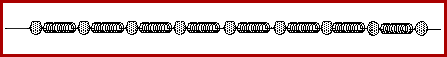
The above animation portrays a medium as a series of particles
connected by springs. As one individual particle is disturbed, it
transmits the disturbance to the next interconnected particle. This
disturbance continues to be passed on to the next particle. The
result is that energy is transported from one end of the medium to
the other end of the medium without the actual tranport of matter. In
this type of wave - a longitudinal wave - the particles of the medium
move in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport.
For more information on physical descriptions of waves,
visit
The
Physics Classroom. Specific information is available there on the
following topics:
Other animations can be seen at the
Multimedia
Physics Studios. Other useful resources regarding the physics of
motion and waves is available through the
Glenbrook
South Physics Home Page.
This page was created by
Tom
Henderson of
Glenbrook South
High School.
Comments and suggestions can be sent by e-mail to
Tom
Henderson.
This page last updated on 3/12/98.
